As the urgency to address climate change intensifies, Australia is at the forefront of adopting renewable energy sources. Harnessing wind, solar, and hydroelectric power is crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to a more sustainable energy system. However, integrating these renewable energy sources into Australia’s existing electricity grid presents a unique set of challenges. This article explores the main obstacles faced in grid integration and discusses potential solutions to enhance the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy in Australia.
The Landscape of Renewable Energy in Australia
Australia has a wealth of renewable energy resources. As reported by the Clean Energy Council, renewable energy constituted nearly 40% of the country’s total electricity generation in 2024, a figure that continues to rise. The landscape is becoming increasingly populated with large-scale solar and wind farms, enhancing the nation’s energy portfolio. Nevertheless, this swift expansion comes with its own set of challenges.
Challenges of Grid Integration
1. Variability and Intermittency
A significant challenge in integrating renewable energy in Australia is the variability and intermittency of these sources. Solar and wind energy are not stable; their production varies with weather conditions and time of day. This fluctuation can lead to grid instability if not properly managed. While large-scale projects aim to provide steady power generation, the unpredictable nature of renewables means that grid operators need to develop strategies to balance supply and demand effectively.
Solutions to Variability
To address the challenges related to variability, various strategies can be implemented:
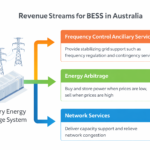
- Energy Storage Solutions: Investing in cutting-edge battery storage technologies allows for the capture of surplus energy produced during peak generation times for deployment during low generation periods. This approach enhances grid stability and provides a more dependable supply of renewable energy.
- Varied Energy Sources: By utilizing a combination of different renewable energy sources, grid operators can lessen their reliance on a single source. For example, integrating wind and solar energy can create a more consistent supply since these sources often complement each other throughout different times of the day and across seasons.
2. Infrastructure Limitations
Australia’s electrical infrastructure, which was predominantly designed for fossil-fuel-based energy generation, is not fully prepared to manage the increasing volume of renewable energy. Upgrades or expansions to the transmission network may be necessary to support new large-scale renewable projects, especially those situated in remote regions rich in resources.
Solutions for Infrastructure
Tackling infrastructure limitations is essential for improving grid integration. Possible solutions include:
- Upgrading Transmission Lines: Investing in high-capacity transmission lines can enhance the efficient transfer of renewable energy from remote generation locations to urban areas. Initiatives like the ‘Hornsdale Power Reserve’ in South Australia exemplify how integrating storage with generation can showcase the advantages of upgrading infrastructure.
- Decentralized Energy Systems: Encouraging local energy generation can alleviate some of the burdens on transmission infrastructure. Community solar projects and smaller wind installations can deliver energy nearer to where it is consumed, thus minimizing transmission losses and reducing strain on the infrastructure.
3. Regulatory and Market Challenges
The existing regulatory framework in Australia can impede the rapid integration of renewable energy. The electricity market is frequently not structured to adapt to the quickly changing landscape of renewable technologies, leading to obstacles for new participants in the energy sector.
Solutions for Regulatory Hurdles
To effectively manage the regulatory environment, several strategies can be adopted:
- Revising Regulatory Frameworks: Policymakers need to evaluate and modify current regulations to foster a more supportive atmosphere for renewable energy integration. Simplifying the approval processes for new projects can help minimize delays and stimulate investment.
- Reforming Market Structures: Establishing market mechanisms that appropriately value renewable energy generation—such as capacity markets or flexible pricing models—can draw in additional investment for large-scale renewable projects.
4. Skills and Workforce Development
As the shift toward renewable energy gains momentum, there is an increasing demand for a skilled workforce familiar with the new technologies involved in renewable energy projects. Transitioning from conventional energy systems to renewables necessitates the development of training programs and educational resources.
Workforce Solutions
Developing a skilled workforce requires the following:
- Education and Training Initiatives: Partnerships among government, educational institutions, and industry participants can facilitate the creation of specialized training programs that provide workers with essential skills in renewable energy technologies.
- Vocational Training: Funding vocational training programs can help cultivate a workforce that meets the needs of the renewable energy sector, ensuring that local communities reap the benefits from job opportunities associated with large-scale renewable energy projects.
Case Studies
1. Hornsdale Power Reserve
The Hornsdale Power Reserve in South Australia is among the world’s largest battery storage facilities, showcasing the effectiveness of storage solutions in integrating renewables into the grid. It has effectively delivered frequency control services, improving grid stability while facilitating a rise in wind energy generation.
2. Snowy 2.0 Project
The Snowy 2.0 project seeks to enhance Australia’s current hydroelectric capabilities by introducing pumped hydro storage. This initiative will greatly increase the capacity for storing renewable energy, offering a dependable backup during times of reduced generation.
Conclusion
The integration of renewable energy in Australia poses challenges that necessitate innovative solutions and cooperative efforts from all parties involved. As the country remains dedicated to lowering carbon emissions and moving towards a sustainable energy future, it is essential to address issues related to variability, infrastructure constraints, regulatory barriers, and workforce training.
By investing in energy storage technologies, enhancing transmission infrastructure, reforming market frameworks, and building a skilled workforce, Australia can establish a strong renewable energy sector. The opportunities for large-scale renewable projects are vast, and with effective strategies in place, Australia can not only integrate these energy sources but also take a leadership role in promoting a renewable energy future, inspiring other countries to do the same.
In conclusion, while the challenges of integrating renewable energy into Australia’s grid are considerable, they are not unmanageable. Through collaboration and commitment across various sectors, the goal of achieving a greener and more sustainable energy landscape can be realized.