Solar Energy Driving Australia’s Transition
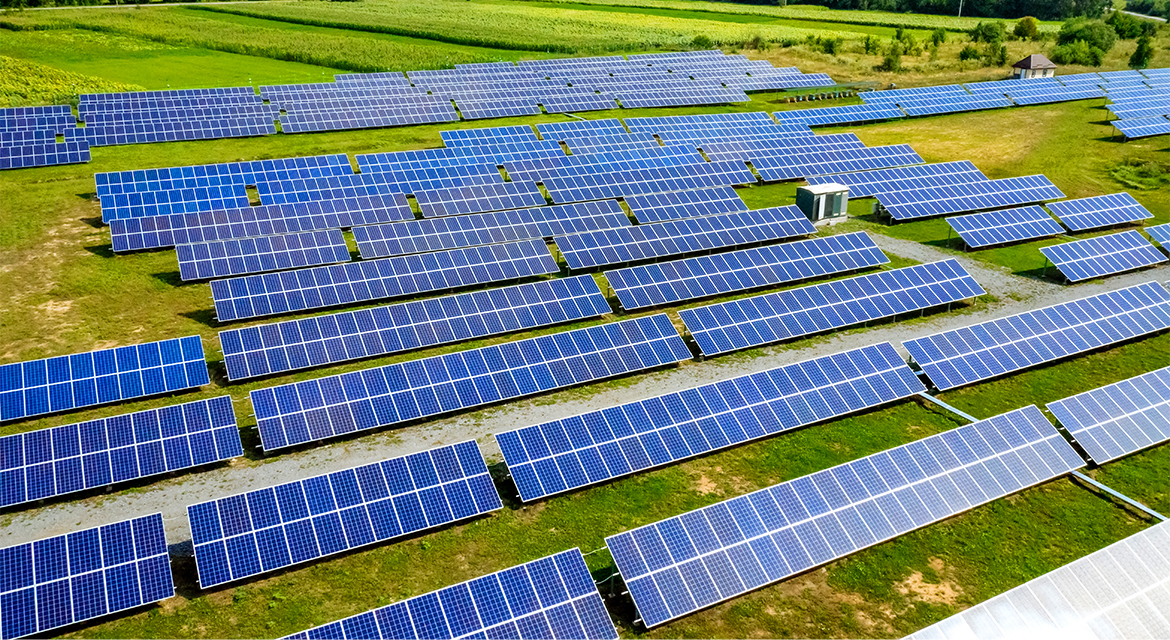
Australia, known for its vast landscapes and abundant sunshine, is becoming a global leader in harnessing solar energy to power its sustainable future. As the world grapples with the urgent need to combat climate change, Australia stands at a critical juncture, leveraging utility-scale solar and Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) to propel its transition towards net-zero emissions. Australia has witnessed a solar revolution, with utility-scale solar projects sprouting across the continent. These vast solar farms, equipped with advanced photovoltaic technology, are capable of generating clean, renewable electricity on a massive scale, significantly reducing carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
This article provides an overview of how utility-scale solar and BESS are shaping Australia’s transition to net-zero emissions while incorporating relevant details about current projects, economic impacts, challenges, and future prospects.
Let’s delve into how the integration of utility-scale solar and BESS technologies is playing a pivotal role in reshaping Australia’s energy landscape.
The Current State of Solar Energy in Australia
Australia has one of the highest rates of solar energy adoption globally, with over 3 million households equipped with solar panels. The country’s solar capacity has surged, driven by declining costs and supportive government policies. According to the Clean Energy Council, Australia’s total installed solar capacity reached over 25 gigawatts (GW) by 2023, with utility-scale solar farms contributing significantly to this growth.
Utility-scale solar projects, which generate electricity on a large scale for distribution to the grid, are becoming increasingly important. These projects not only provide substantial amounts of renewable energy but also help reduce reliance on fossil fuels, thereby lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Driving Towards Net-Zero
Amid mounting concerns over climate change and the imperative to achieve net-zero emissions, Australia is accelerating its renewable energy transition. Utility-scale solar plays a central role in this paradigm shift, offering a sustainable solution to power the nation’s homes, industries, and infrastructure. By harnessing the power of the sun, Australia is forging a path towards a greener and more resilient energy future.
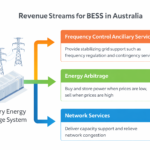
The Role of Battery Energy Storage Systems
While solar energy is abundant during the day, its intermittent nature poses challenges for consistent power supply. This is where Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) come into play. BESS technologies store excess solar energy generated during peak production hours and release it when demand is high or during periods of low sunlight. By integrating BESS with utility-scale solar projects, Australia is revolutionizing its energy grid, enhancing efficiency, reliability, and resilience.
Importance of Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
– Grid Stability: BESS plays a crucial role in stabilizing the grid by storing excess energy generated during peak sunlight hours and releasing it during demand spikes.
– Integration Challenges: While solar energy is abundant, its intermittent nature poses challenges. BESS helps mitigate these issues by providing a reliable energy supply.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
The integration of utility-scale solar and BESS offers a myriad of benefits to Australia. From job creation and economic growth to reduced carbon emissions and energy security, the shift towards renewable energy sources not only mitigates climate change but also fosters a more sustainable and prosperous future for the country. By investing in solar energy infrastructure, Australia is not only safeguarding its environment but also reaping the economic.
The transition to utility-scale solar and BESS is not only environmentally beneficial but also economically advantageous for Australia:
– Job Creation: The renewable energy sector is creating thousands of jobs across Australia, from manufacturing to installation and maintenance.
– Investment Opportunities: Increased investment in utility-scale solar and BESS is attracting both domestic and international investors, fostering economic growth.
Australia’s Success Stories
Several pioneering utility-scale solar and BESS projects in Australia exemplify the country’s commitment to sustainable energy solutions.
– Hornsdale Power Reserve: One of the most significant examples of successful BESS integration in in South Australia. With a capacity of 150 megawatts (MW), it is one of the largest lithium-ion battery installations globally. The facility has demonstrated its ability to provide essential services to the grid, including frequency control and emergency backup power. Since its launch in 2017, it has not only contributed to reducing electricity prices but has also proven that large-scale battery storage can be economically viable. The project has set a benchmark for future developments in both solar and battery technologies.
– Kidston Solar Farms in Queensland: a landmark project that combines a solar farm with a pumped hydro storage system. This innovative approach allows excess solar energy to be stored as potential energy in water reservoirs, which can then be converted back into electricity when needed. This hybrid model showcases how integrating different renewable technologies can enhance overall efficiency and reliability.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the progress made, several challenges remain on Australia’s path to net-zero:
1. Infrastructure Development: Upgrading existing grid infrastructure to accommodate increased renewable energy generation is crucial for ensuring reliability.
2. Policy Frameworks: Continued government support through incentives and regulations will be necessary to encourage investment in renewable technologies.
3. Public Acceptance: Engaging local communities and addressing concerns about new projects will be vital for successful implementation.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, Australia has set ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 43% below 2005 levels by 2030 as part of its commitment under the Paris Agreement. Achieving these goals will require a significant increase in both utility-scale solar capacity and BESS deployment.
Technological Innovations
Ongoing advancements in battery technology are expected to enhance efficiency and reduce costs further. Innovations such as solid-state batteries and alternative chemistries hold promise for increasing storage capacity while minimizing environmental impacts.
Conclusion
The integration of utility-scale solar and battery energy storage systems represents a critical pathway for Australia as it strives toward net-zero emissions by 2050. By leveraging its abundant solar resources and investing in innovative storage solutions, Australia can not only meet its energy needs sustainably but also position itself as a leader in the global renewable energy landscape.
As we move forward, collaboration among governments, industry stakeholders, and local communities will be essential to overcome challenges and fully realize the potential of solar energy in achieving a cleaner and greener future.